PV module
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
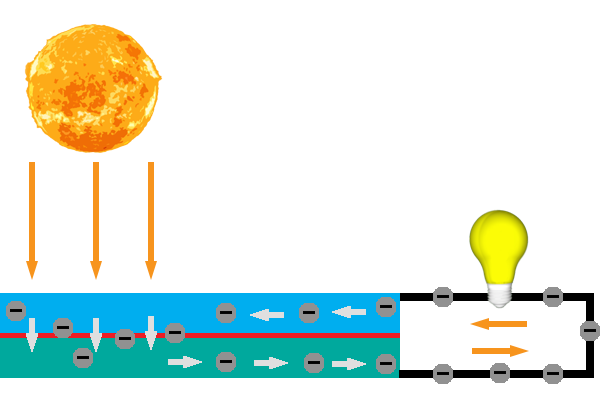
Solar PV modules use the photovoltaic (PV) effect, which enables them to generate electrical current in upon exposure to light. PV modules are composed of individual cells wired together, current is generated when light hits one side of the cell and excites electrons that then pass through a one-way barrier forcing them to flow through a circuit to return to their point of origin. These electrons carry energy which can be used to power loads. There are many different technologies available and ways to design a system that can meet needs that range from simple lighting, to running appliances, powering machinery and pumping water. A typical solar cell produces around .5V while producing current.
Common module configurations
- A 36-cell module comprised of .5V cells would have a rated voltage of around 18V.
- A 60-cell module comprised of .5V cells would have a rated voltage of around 30 volts.
- A 72-cell module comprised of .5V cells would have a rated voltage of around 36V.