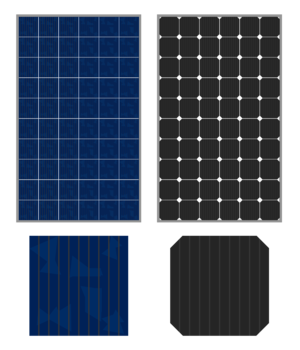
PV module
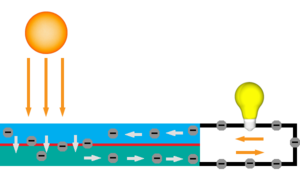
Solar PV modules use the photovoltaic (PV) effect, which enables them to generate electrical current in upon exposure to light. PV modules are composed of individual cells wired together, current is generated when light hits one side of the cell and excites electrons that then pass through a one-way barrier forcing them to flow through a circuit to return to their point of origin. A typical solar cell produces around .5V when exposed to sufficient light. These movement of these electrons can be used to to do work or power loads. There are many different technologies available and ways to design a system that can meet needs that range from simple lighting, to running appliances, pumping water or powering cities.
Types
There are many different chemstries that are used in PV cells, but there are two main categories of modules that are found on the market. Each type of solar module continues to have different characteristics that can be attractive depending upon the circumstances such as lower price or higher efficiency.
- One Crystalline silicon modules
- The most common type of module on the market. These modules can come in poly or monocrystalline construction. The names are derived from the way that they are manufactured with monocrystalline cells being cut from a single crystal and polycrystalline cells being comprised of silicon from various crystals. Both types are are composed of a few simple materials (average by weight): 76% glass (panel surface), 10% polymer (encapsulant and backsheet foil), 8% aluminium (mostly the frame), 5% silicon (solar cells), 1% copper (interconnectors) and less than 0.1% silver (contact lines) and other metals (mostly tin and lead) [1]
- Monocrystalline modules are more expensive, but achieve higher average efficiencies around 17-20%.
- Polycrystalline modules are less expensive and are less efficient with average efficiencies around 16-17%.
- The most common type of module on the market. These modules can come in poly or monocrystalline construction. The names are derived from the way that they are manufactured with monocrystalline cells being cut from a single crystal and polycrystalline cells being comprised of silicon from various crystals. Both types are are composed of a few simple materials (average by weight): 76% glass (panel surface), 10% polymer (encapsulant and backsheet foil), 8% aluminium (mostly the frame), 5% silicon (solar cells), 1% copper (interconnectors) and less than 0.1% silver (contact lines) and other metals (mostly tin and lead) [1]
- Two Thin film modules
- Thin film modules are built out by laying photovoltaic material in one or more layers on a supporting material such as glass, plastic, or metal. Thin film modules come in various types with Cadmium-Telluride (CdTe) Being the most common. CdTe modules contain far less aluminum and more glass than Crystalline silicon modules (average by weight): 97% glass (panel surface), ~3% polymer (junction boxes and sealant) and negligible amounts of semiconductors and metals. [1] Thin film modules are far less efficient than crystalline silicon modules at around 9% efficiency, but significantly cheaper.
Characteristics
Solar modules are rated in terms of Watts (W) under industry determined laboratory test conditions called Standard Test Conditions (STC). These conditions are:
- 1000W/m² of irradiance which is a measurement of sunlight intensity
- 25C cell temperature
- An airmass of 1.5
A module is tested and rated based upon the following values which can be found printed on the module or in its specifications sheet:
- Open Circuit Voltage (Voc) – The voltage that the module will produce under STC when it is not connected to a circuit.
- Short Circuit Current (Isc) – The current that a module will produce under STC when it is short circuited or with its positive output directly connected to its negative.
- Maximum Power Voltage (Vmp) – The voltage that the module will produce when connected to a circuit under STC.
- Maximum Power Current (Imp) – The current that the module will produce when connected to a circuit under STC.
Solar modules will only produce their rated power at their Maximum Power Point, which is Vmp multiplied by Imp, under laboratory test conditions where are not very frequently reached in the real world. Cell temperatures rise quickly when exposed to sun and 1000W/m² is on a clear sunny day. Higher cell temperatures decrease cell voltage and conversely lower cell temperatures can increase cell voltage beyond. Lower irradiance reduces cell current and higher irradiance increases cell current.
Common module configurations
- A 36-cell module comprised of .5V cells would have a rated voltage of around 18V.
- A 60-cell module comprised of .5V cells would have a rated voltage of around 30 volts.
- A 72-cell module comprised of .5V cells would have a rated voltage of around 36V.
Projected life
A well-made silicon solar module will continue functioning over 25 years, although all modules degrade with the passage of time. High-quality modules degrade at an average rate of .5% to 1% per year, whereas poorly made modules degrade even quicker. This is the primary difference between the different costs and qualities of modules.
Maintenance
There are no moving parts in solar PV modules and they are built out of durable materials. The only maintenance that is likely to ever be required a module is an occasionally cleaning if the module is in an area that lacks regular rainfall.
Recyclability
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 IRENA End-of-Life Management Solar Photovoltaic Panels. https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2016/IRENA_IEAPVPS_End-of-Life_Solar_PV_Panels_2016.pdf