Difference between revisions of "Basic stand-alone PV system components"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:Basics]] | [[Category:Basics]] | ||
| − | Stand-alone PV systems, regardless of where one is at in the world, share the same basic components. | + | Stand-alone PV systems, regardless of where one is at in the world, share the same basic components. This article will give a high level overview with links to more detailed information on each component. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
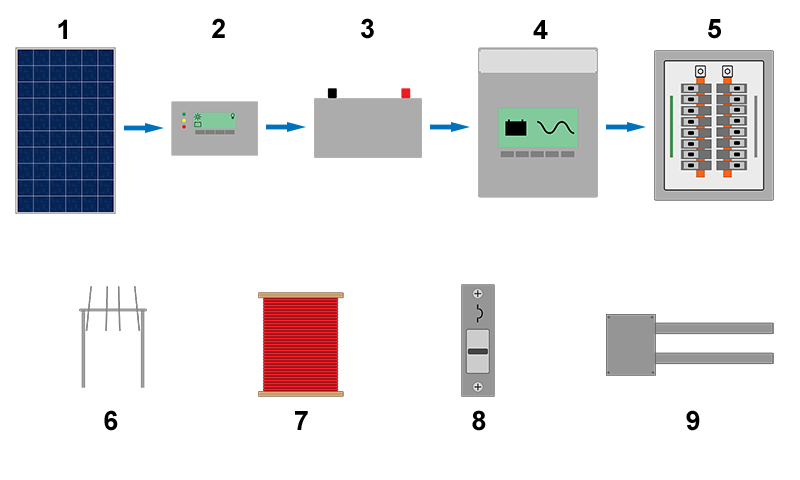
| + | [[File:Components of a pv system-2009232.png|frame|center|'''Components of a stand-alone system with an inverter.''' Components in this image: '''1.''' Solar module/array '''2.''' Charge controller '''3.''' Battery bank ''' 4. '''Inverter''' 5.''' Distribution panel to feed loads '''6.''' Mounting structure '''7.''' Wire '''8.''' Overcurrent protection '''9.''' Physical wire protection]] | ||
==Solar PV modules== | ==Solar PV modules== | ||
| + | A PV system has one or more modules that convert the energy of the sun into electrical current. Solar PV modules use the photovoltaic (PV) effect to generate electrical current upon exposure to light. If there are multiple modules in the system, they are typically arranged into what is referred to as an ''array.'' Throughout the rest of this website we will use the term array even if there is just one module. | ||
==Batteries== | ==Batteries== | ||
| + | A stand-alone PV system requires some type of storage system in order to provide energy at night or during periods of bad weather. Batteries are durable and reliable form of storage. Other forms of storage exist, but they are rare. The focus here will be on battery-based systems. If there are multiple batteries in a system they are arranged together into what is referred to as a ''battery bank.'' Throughout the rest of this website we will use the term battery bank even if there is just one battery. | ||
==Charge controllers== | ==Charge controllers== | ||
| + | Batteries have specific charging requirements and proper charging to essentially to ensuring that they have a long life. In all systems with batteries it is necessary to have a charge controller or an inverter-charger that is capable of properly regulation the charging of the battery bank. A system may have multple parallel charging sources as well. | ||
==Inverters== | ==Inverters== | ||
| + | In order to power alternating current loads, it is necessary to have an inverter in a stand-alone system. The battery bank provides a stable voltage and current to the inverter, which it can then convert into stable alternating current to supply AC loads. | ||
==Mounting systems== | ==Mounting systems== | ||
| + | PV modules must be anchored to some type of mounting system to ensure that their production is maximized with the correct orientation and angle relative to the sun, but also to ensure that they are not damaged by weather. | ||
==Wires== | ==Wires== | ||
| + | All of the different electrical components of a system need to be connected together with wire that is appropriate for the voltage, current and conditions to which it will be subjected. | ||
==Overcurrent protection== | ==Overcurrent protection== | ||
| + | All wires have a maximum rated current that they can handle. If this number is exceeded, an electrical fire can result. If a wire could potentially be supplied with more current than it can handle, then it is necessary to protect it with an overcurrent protection device such as a breaker or fuse. | ||
==Physical wire protection== | ==Physical wire protection== | ||
| + | Wires have specific conditions in which they can be installed. If a wire could potentially be damaged by weather, rodents, building occupants or any other source , it is necessary to protect the wire with some type of conduit. | ||
Revision as of 10:12, 23 September 2020
Stand-alone PV systems, regardless of where one is at in the world, share the same basic components. This article will give a high level overview with links to more detailed information on each component.
Contents
Solar PV modules
A PV system has one or more modules that convert the energy of the sun into electrical current. Solar PV modules use the photovoltaic (PV) effect to generate electrical current upon exposure to light. If there are multiple modules in the system, they are typically arranged into what is referred to as an array. Throughout the rest of this website we will use the term array even if there is just one module.
Batteries
A stand-alone PV system requires some type of storage system in order to provide energy at night or during periods of bad weather. Batteries are durable and reliable form of storage. Other forms of storage exist, but they are rare. The focus here will be on battery-based systems. If there are multiple batteries in a system they are arranged together into what is referred to as a battery bank. Throughout the rest of this website we will use the term battery bank even if there is just one battery.
Charge controllers
Batteries have specific charging requirements and proper charging to essentially to ensuring that they have a long life. In all systems with batteries it is necessary to have a charge controller or an inverter-charger that is capable of properly regulation the charging of the battery bank. A system may have multple parallel charging sources as well.
Inverters
In order to power alternating current loads, it is necessary to have an inverter in a stand-alone system. The battery bank provides a stable voltage and current to the inverter, which it can then convert into stable alternating current to supply AC loads.
Mounting systems
PV modules must be anchored to some type of mounting system to ensure that their production is maximized with the correct orientation and angle relative to the sun, but also to ensure that they are not damaged by weather.
Wires
All of the different electrical components of a system need to be connected together with wire that is appropriate for the voltage, current and conditions to which it will be subjected.
Overcurrent protection
All wires have a maximum rated current that they can handle. If this number is exceeded, an electrical fire can result. If a wire could potentially be supplied with more current than it can handle, then it is necessary to protect it with an overcurrent protection device such as a breaker or fuse.
Physical wire protection
Wires have specific conditions in which they can be installed. If a wire could potentially be damaged by weather, rodents, building occupants or any other source , it is necessary to protect the wire with some type of conduit.