Difference between revisions of "Busbar/es"
(Created page with "File:Busbar2011292.png|thumb|right|''(1),(2)'' - Ejemplos de diferentes diseños de embarrados desde diferentes perspectivas. <br /> ''(3)'' - La cantidad de corriente que p...") |
(Created page with "Los embarrados son un componente esencial de los sistemas eléctricos, ya que permiten conexiones en paralelo de circuitos de forma...") |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
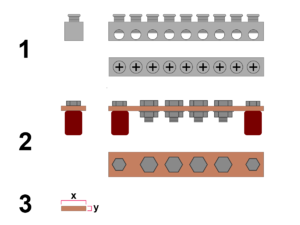
[[File:Busbar2011292.png|thumb|right|''(1),(2)'' - Ejemplos de diferentes diseños de embarrados desde diferentes perspectivas. <br /> ''(3)'' - La cantidad de corriente que puede manejar un embarrado depende de su grosor.]] | [[File:Busbar2011292.png|thumb|right|''(1),(2)'' - Ejemplos de diferentes diseños de embarrados desde diferentes perspectivas. <br /> ''(3)'' - La cantidad de corriente que puede manejar un embarrado depende de su grosor.]] | ||
| − | + | Los embarrados son un componente esencial de los sistemas eléctricos, ya que permiten [[Special:MyLanguage/Series and parallel|conexiones en paralelo]] de circuitos de forma segura y sencilla. Hay muchos diseños diferentes de embarrados que tienen el mismo propósito. Es importante que cualquier embarrado utilizado esté clasificada para manejar la corriente que debe transportar y que el embarrado esté correctamente aislada de todos los otros componentes del sistema. Los embarrados solo deben instalarse dentro de gabinetes que estén protegidos contra el acceso no autorizado o accidental, ya que tienen partes expuestas bajo tensión. | |
The amount of current that a standard copper busbar can carry can be determined by measuring the height and width of the busbar in mm - see ''3'' illustration. If these two values are multiplied it will give a mm² value that can be used with the table for wire ampacity in [[Special:MyLanguage/Overview of wire and overcurrent protection sizing and selection|Overview of wire and overcurrent protection sizing and selection]]. | The amount of current that a standard copper busbar can carry can be determined by measuring the height and width of the busbar in mm - see ''3'' illustration. If these two values are multiplied it will give a mm² value that can be used with the table for wire ampacity in [[Special:MyLanguage/Overview of wire and overcurrent protection sizing and selection|Overview of wire and overcurrent protection sizing and selection]]. | ||
Revision as of 11:25, 12 February 2021
Los embarrados son un componente esencial de los sistemas eléctricos, ya que permiten conexiones en paralelo de circuitos de forma segura y sencilla. Hay muchos diseños diferentes de embarrados que tienen el mismo propósito. Es importante que cualquier embarrado utilizado esté clasificada para manejar la corriente que debe transportar y que el embarrado esté correctamente aislada de todos los otros componentes del sistema. Los embarrados solo deben instalarse dentro de gabinetes que estén protegidos contra el acceso no autorizado o accidental, ya que tienen partes expuestas bajo tensión.
The amount of current that a standard copper busbar can carry can be determined by measuring the height and width of the busbar in mm - see 3 illustration. If these two values are multiplied it will give a mm² value that can be used with the table for wire ampacity in Overview of wire and overcurrent protection sizing and selection.
The formula for calculating the cross-sectional area of a busbar is:
| Cross sectional area | = x (width) × y (height) |
|---|
Example 1: A busbar is measured to have a height of 5 mm and a width of 10 mm. What is its mm² cross sectional area? At 75°C how much current can it carry?
- Cross sectional area = 5 mm × 10 mm
- Cross-sectional area = 50 mm²
- 50 mm² can carry 130 A at 75°C according to the conductor ampacity table.