Difference between revisions of "Charge controller"
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
===Pulse width modulation (PWM)=== | ===Pulse width modulation (PWM)=== | ||
| − | + | A PWM charge controller measures the voltage of the battery bank and the temperature (ambient or at the battery bank) to estimate the state of charge of the battery and regulate charging. This type of charge controller can only limit the amount of current that is supply to the battery bank and not the voltage of the battery bank or PV source. The PV source may be capable of operating at a higher voltage and supplying more power, but this type of charge controller does not offer this functionality. | |
As the charge controller cannot regulate the voltage of PV source, the modules/array must be designed to work with the voltage of the battery bank. This means that the PV source will have to operate at a relatively low voltage. There are limited module configurations that will work properly with a PWM charge controller: | As the charge controller cannot regulate the voltage of PV source, the modules/array must be designed to work with the voltage of the battery bank. This means that the PV source will have to operate at a relatively low voltage. There are limited module configurations that will work properly with a PWM charge controller: | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
*A 72 cell module is referred to as a 24V nominal module and will be able to supply an appropriate voltage to a 24V battery bank. These modules can be put in parallel to supply more power for a 24V battery bank or can be connected in series (2 per series string for a 48V battery bank). | *A 72 cell module is referred to as a 24V nominal module and will be able to supply an appropriate voltage to a 24V battery bank. These modules can be put in parallel to supply more power for a 24V battery bank or can be connected in series (2 per series string for a 48V battery bank). | ||
| − | '''Ratings''' | + | '''Ratings'''<br/> |
| − | + | A PWM charge controller will be rated in terms of nominal system voltage and maximum current. It is assumed that the system designer will choose the appropriate PV source configuration based upon nominal voltage of the battery bank. | |
| − | + | *Nominal system voltage: 12V, 24V, 48V | |
| + | *Maximum PV source current: 6A-60A | ||
===Maxmimum power point tracking (MPPT)=== | ===Maxmimum power point tracking (MPPT)=== | ||
| + | A MPPT charge controller works similarly to a PWM charge controller in that it measures voltage of the battery and temperature to determine state of charge and regulate charging. The difference is that an MPPT charge controller can control the voltage of the PV source and the voltage that it supplies to the battery bank using more sophisticated technology and electronics. This can permit higher system performance under a more variable range of conditions and configurations. An MPPT charge controller can accept a variety of different module types and series/parallel configurations. | ||
| − | + | '''Ratings'''<br/> | |
| + | A MPPT charge controller will be rated in terms of nominal system voltage, maximum PV source voltage, minimum PV source voltage and maximum PV source current. A system designer will have to design the PV source properly to be able to work within these parameters. | ||
| + | *Nominal system voltage: 12V, 24V, 48V | ||
| + | *Maximum PV source voltage: varies up to 600V | ||
| + | *Minimum PV source voltage: depends upon nominal voltage and charge controller type | ||
| + | *Maximum PV source current: up to 100A+ | ||
| − | + | ==PWM vs MPPT comparison== | |
| − | + | The right charge controller for every application must be decided upon a variety of different factors: | |
| − | in | + | #Budget - A MPPT charge controller may cost 1.5-2 times as much as a PWM charge controller, although there may be significant savings when designing a system by using a standard module size (60 cell or 72 cell) rather than 36 cell modules. |
| − | + | #Component availability - Certain charge controller types or module types may not be readily available in all locations. | |
| − | controller. | + | #Performance - MPPT charge controller will perform better in cooler climates as they can take advantage of the higher voltage that a PV is capable of producing. |
| − | + | #System size - With a smaller system a the advantages of a PWM charge controller prevail, but as system size increases the benefits of a MPPT charge controller increase. At a certain system size the additional wiring required with a PWM charge controller due to parallel connections and low voltage becomes a significant pain and expense. | |
| + | ==Additional charge controller features== | ||
| + | |||
| + | User interface – The health and longevity of a solar system depend upon the end user being able to properly | ||
| + | assess the state of charge of their batteries and adjust their usage accordingly. The state of charge of a battery | ||
| + | should be easily displayed and understandable to end users. | ||
| + | Lighting controls – If the system is intended to run DC lighting, selecting a charge controller with lighting control | ||
| + | is recommended. Charge controllers with this functionality will turn off the lights if the battery voltage is too low | ||
| + | in order to protect them and will protect against short circuits as the charge controller limits current to the lights. | ||
| + | Additionally, some can be set to turn off/on lights during certain hours. | ||
| + | Monitoring – Monitoring capabilities are an option for many different charge controllers. Some charge controllers | ||
| + | internally log and store data and others rely on communications technology to be able to export the data (cell | ||
| + | service or internet). Monitoring is useful to evaluate the performance of different designs, the weather conditions | ||
| + | in a given environment and how the end user is treating the system. | ||
| + | Temperature sensor – The temperature of batteries significantly affects the voltage, the perceived state of charge | ||
| + | and therefore battery charging. Better quality charge controllers will offer the option of having a temperature | ||
| + | probe that can be used to adjust charging parameters according to the battery temperature. | ||
== Projected life == | == Projected life == | ||
Revision as of 08:56, 15 October 2020
The charge controller in an off-grid PV system serves as the connection point between the PV source and the energy storage system. Every type of energy storage has specific charging and discharging preferences that must be taken into account to ensure that a long life (See the article on lead acid batteries for specific details). The charge controller works to manage the incoming power from the PV source to maximize charging when the batteries can accept it and to reduce it when batteries begin nearing full. Overcharging a battery will cause the chemicals and materials in battery to breakdown and generate significant amounts of heat, which will lead to reduced battery life or permanent damage to the battery. Chronic undercharging of a battery is more common and occurs when a battery is not allowed to return to a full state of charge on a regular basis, which will lead to a build up of sulfation on the lead plates inside of the battery which over time will reduce battery life. A charge controller often cannot protect an energy storage system from over-discharge due to the operation of loads, an off-grid system should always include a low voltage disconnect that is integrated into the charge controller, inverter or is a seperate piece of equipment.
There are a variety of different charge controller designs on the market that vary greatly in voltage/current capacity, performance, functionality and cost. Investing in a quality charge controller will ensure the longevity of the other components in an off-grid PV system.
Contents
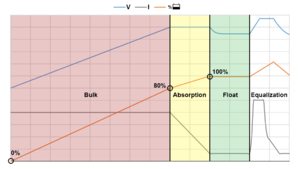
Charging phases
All battery chargers for lead acid batteries, not just charge controllers for PV systems, follow the same basic three stage charging pattern: bulk, absorption and float. A charge controller moves through these different stages based upon programmed voltage set points and the ambient battery temperature or ambient temperature. Smaller capacity and lower cost charge controllers may not offer the capability to program the voltage set points and will rely on values set by the manufacturer. If the charge controller does enable the programming of the voltage set points, the user manual for that specific battery should be consulted as the voltage set points vary based upon manufacturer and battery type (FLA, AGM, GEL).
Bulk phase
When a battery is between 0-80% state of charge, the charge controller will send the full current of the PV source to the battery bank to bring the voltage of the system up. The charge controller will continue supplying full current in bulk mode until a certain voltage is reached, which is typically around 14.6-14.8V for a lead acid battery.
Absoprtion phase
As the battery becomes more full at around 80% of capacity, the charge controller switches to absorption mode at which point it attempts to hold the battery bank at the maximum voltage achieved during the bulk charging phase (~14.4-14.8V for a 12V lead acid battery) using the minimum amount of current necessary to do so. As the battery becomes more full, the amount of current required to hold it at the fixed voltage decreases. The charge controller will continue in this mode until either a set amount of time has passed or the amount of current required to hold the battery bank at a fixed voltages decreases to a programmed minimum. This typically occurs at around 95% of battery capacity.
Float phase
A battery nearing complete charge can no longer accept as much current, so the charge controller moves into the float phase, which means that it tries to hold the battery bank at a lower voltage (~13.2-13.8V for a 12V lead acid battery) using the minimum amount of current necessary. The slow gradually charge can bring the batteries up to a 100% state of charge.
Equalization charge
An equalization charge is not a standard charging phase, it is a planned over-charge of the batteries that can help to reduce the long-term deterioration of batteries due to a build up of sulfation on the lead plates inside. The voltage of the battery bank may be increased as high as ~16.2V for a specified period of time. Not all charge controllers have this capability. Only flooded lead acid batteries can undergo an equalization charge. The user must either schedule or activate an equalization charge and it should only be done a day with abundant sun as the over-charge will require more energy than normal.
Charge controller types
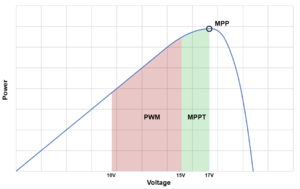
There are two main types of charge controllers used in off-grid PV installations: pulse width modulation (PWM) and maximum power point tracking (MPPT). Both types of charge controllers continue to be popular as each as distinct advantages depending upon the application.
Pulse width modulation (PWM)
A PWM charge controller measures the voltage of the battery bank and the temperature (ambient or at the battery bank) to estimate the state of charge of the battery and regulate charging. This type of charge controller can only limit the amount of current that is supply to the battery bank and not the voltage of the battery bank or PV source. The PV source may be capable of operating at a higher voltage and supplying more power, but this type of charge controller does not offer this functionality.
As the charge controller cannot regulate the voltage of PV source, the modules/array must be designed to work with the voltage of the battery bank. This means that the PV source will have to operate at a relatively low voltage. There are limited module configurations that will work properly with a PWM charge controller:
- A 36 cell module is referred to as a 12 volt nominal module and will be able to supply an appropriate voltage to a 12V battery bank. These modules can be put in parallel to supply more power for a 12V battery bank or can be connected together in series (2 per series string for 24V battery bank and 4 per series string for a 48V battery bank).
- A 72 cell module is referred to as a 24V nominal module and will be able to supply an appropriate voltage to a 24V battery bank. These modules can be put in parallel to supply more power for a 24V battery bank or can be connected in series (2 per series string for a 48V battery bank).
Ratings
A PWM charge controller will be rated in terms of nominal system voltage and maximum current. It is assumed that the system designer will choose the appropriate PV source configuration based upon nominal voltage of the battery bank.
- Nominal system voltage: 12V, 24V, 48V
- Maximum PV source current: 6A-60A
Maxmimum power point tracking (MPPT)
A MPPT charge controller works similarly to a PWM charge controller in that it measures voltage of the battery and temperature to determine state of charge and regulate charging. The difference is that an MPPT charge controller can control the voltage of the PV source and the voltage that it supplies to the battery bank using more sophisticated technology and electronics. This can permit higher system performance under a more variable range of conditions and configurations. An MPPT charge controller can accept a variety of different module types and series/parallel configurations.
Ratings
A MPPT charge controller will be rated in terms of nominal system voltage, maximum PV source voltage, minimum PV source voltage and maximum PV source current. A system designer will have to design the PV source properly to be able to work within these parameters.
- Nominal system voltage: 12V, 24V, 48V
- Maximum PV source voltage: varies up to 600V
- Minimum PV source voltage: depends upon nominal voltage and charge controller type
- Maximum PV source current: up to 100A+
PWM vs MPPT comparison
The right charge controller for every application must be decided upon a variety of different factors:
- Budget - A MPPT charge controller may cost 1.5-2 times as much as a PWM charge controller, although there may be significant savings when designing a system by using a standard module size (60 cell or 72 cell) rather than 36 cell modules.
- Component availability - Certain charge controller types or module types may not be readily available in all locations.
- Performance - MPPT charge controller will perform better in cooler climates as they can take advantage of the higher voltage that a PV is capable of producing.
- System size - With a smaller system a the advantages of a PWM charge controller prevail, but as system size increases the benefits of a MPPT charge controller increase. At a certain system size the additional wiring required with a PWM charge controller due to parallel connections and low voltage becomes a significant pain and expense.
Additional charge controller features
User interface – The health and longevity of a solar system depend upon the end user being able to properly assess the state of charge of their batteries and adjust their usage accordingly. The state of charge of a battery should be easily displayed and understandable to end users. Lighting controls – If the system is intended to run DC lighting, selecting a charge controller with lighting control is recommended. Charge controllers with this functionality will turn off the lights if the battery voltage is too low in order to protect them and will protect against short circuits as the charge controller limits current to the lights. Additionally, some can be set to turn off/on lights during certain hours. Monitoring – Monitoring capabilities are an option for many different charge controllers. Some charge controllers internally log and store data and others rely on communications technology to be able to export the data (cell service or internet). Monitoring is useful to evaluate the performance of different designs, the weather conditions in a given environment and how the end user is treating the system. Temperature sensor – The temperature of batteries significantly affects the voltage, the perceived state of charge and therefore battery charging. Better quality charge controllers will offer the option of having a temperature probe that can be used to adjust charging parameters according to the battery temperature.